Solenoid coils are versatile components that are used in a wide range of applications across many different fields. Here are some examples of where solenoid coils are commonly used:
Medical: Solenoid coils are used in medical devices, such as MRI machines, to generate magnetic fields for imaging.
Industrial automation: Solenoid coils are used in industrial automation applications, such as valve control, conveyor systems, and robotics.
Security systems: Solenoid coils are used in security systems, such as door locks and access control systems.
Automotive: Solenoid coils are used in automobiles for a variety of applications, such as fuel injection, transmission control, and engine management.
Find out here which requirements have to be taken into account in the design.
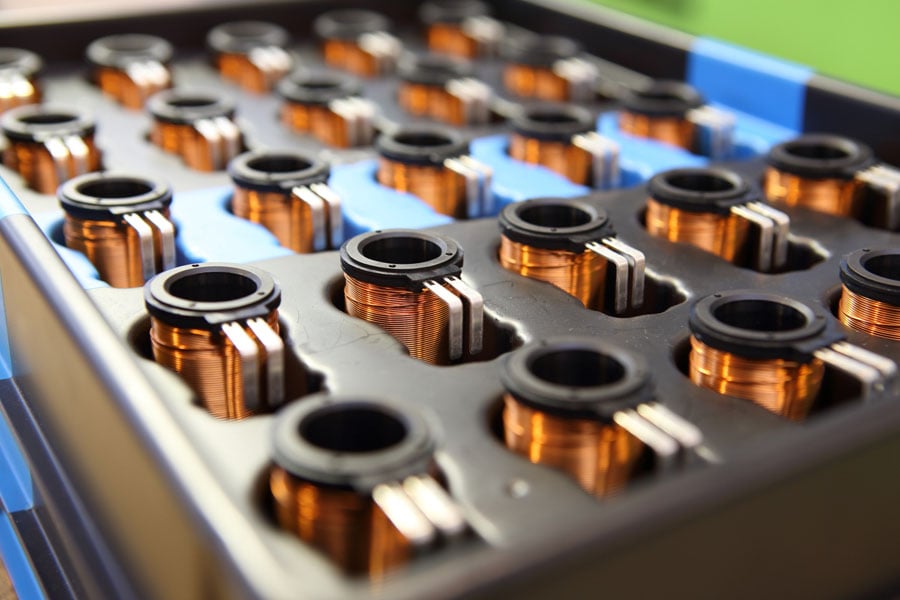

Here's a short summary of the decisive factors of solenoid coils:
Coil geometry: The shape, size, number of turns and fill factor of the coil are critical factors that determine the magnetic field strength and direction.
Material selection: The choice of core material and insulation type can significantly impact the performance of the solenoid coil. Unlike other types of coils, solenoid coils only have one option for conductor material, which is copper.
Operating conditions: The environmental conditions in which the solenoid coil will operate, such as temperature, humidity, and vibration, must be considered when designing and selecting solenoid coils.
Manufacturing constraints: The design of the solenoid coil must take into account manufacturing constraints, such as available space, production costs, and lead time.Electrical properties: The electrical properties of the solenoid coil, such as resistance, inductance, and capacitance, must be optimized for the intended application.
Manufacturing constraints: The design of the solenoid coil must take into account manufacturing constraints, such as available space, production costs, and lead time.
Joining technique: The manner in which the wire is terminated and connected to surrounding components is heavily dependent on the specific application. This crucial aspect is often overlooked, but does significantly impact the overall cost of the solenoid coil.
 Enamelled Wires for Automotive
Enamelled Wires for Automotive
 The Application of Shandong Hu
The Application of Shandong Hu
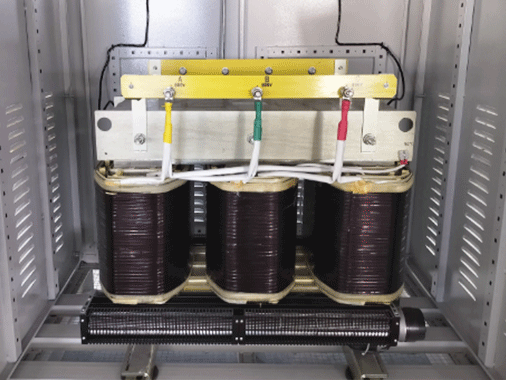 The isolation transformer uses
The isolation transformer uses
 The Application of Shandong Hu
The Application of Shandong Hu